
Vitality Blueprint - Female
$1000 NZD
Vitality testing delivers a comprehensive analysis of the entire body for peak health and performance. It covers 13 functional areas ranging from energy production, to gut health, and hormone profile. Results from this panel are designed for upload to Vitality's bloodwork platform for analysis and personalised health recommendations (learn more at https://www.vitalityblueprint.com/)
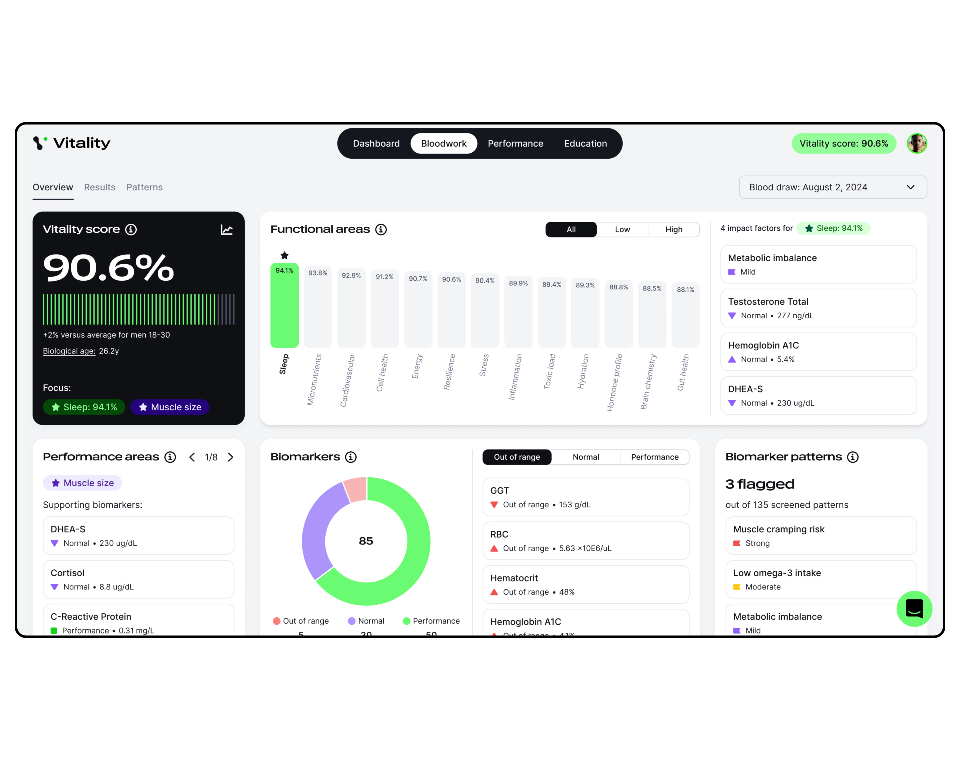
This panel is compatible with the Vitality bloodwork platform which offers personalised bloodwork interpretation and health recommendations to optimise health and performance. i-screen results can be uploaded directly to Vitality for a comprehensive analysis of your entire physiology (covering 13 functional areas) and corresponding health roadmap covering lifestyle, nutrition, and supplement recommendations. Learn more and purchase a plan at vitalityblueprint.com.
What's included
Oestradiol (Day 3)
Adrenal Function (Serum)
Two of the most important hormones that impact athletic performance are cortisol and DHEA, the long-lasting stress hormones produced by the adrenal glands. Cortisol has a catabolic effect which mobilises the body’s nutritional resources for fuel. DHEA has an opposing anabolic effect and coverts food into living tissue. In order to achieve your fitness goals cortisol and DHEA must be in proper balance.
Full Blood Count with differential
The full blood count is used as a broad screening test to check for such disorders as anaemia (decrease in red blood cells or haemoglobin), infection, and many other diseases. It is actually a group of tests that examine different parts of the blood. Results from the following tests provide the broadest picture of your health.
Cholesterol
Lipids and cholesterol are fat-like substances in your blood. Some are necessary for good health, but when you have a high level of cholesterol in your blood, a lot of it ends up being deposited in the walls of your arteries and other vital organs. Lifestyle choices including diet, exercise and alcohol intake can all influence cholesterol levels and your risk of developing heart disease.
Metabolic Markers
With type 2 diabetes glucose builds up in the blood leading to problems with the heart, kidneys, eyes, nerves, and blood vessels. Unlike a regular blood sugar test, the HbA1c blood test is not affected by short-term changes, so even though you may have had high blood sugar on occasion, a good HbA1c result can show that you’re doing a good job of controlling your blood sugar levels over time.
Inflammation
Inadequate recovery from exercise or overtraining can result in inflammation and muscle damage. In addition to c-reactive protein and creatine kinase, this panel also measures homocysteine which is another recognised risk factor for cardiovascular disease, as well as osteoporosis and Alzheimer’s.
Bone Health
Calcium and vitamin D play a critical role in maintaining bone health. When you don’t get enough calcium, you increase your risk of developing osteoporosis and stress fractures. This blood test measures both your total calcium and corrected calcium levels, as well your 25-OHD vitamin D levels.
Red Blood Cell Magnesium
Liver Function (with AST)
Your liver processes drugs and alcohol, filters toxic chemicals, stores vitamins and minerals, and makes bile, proteins and enzymes. This liver function test examines enzymes and other markers for evidence of damage to your liver cells or a blockage near your liver which can impair its function.
Kidney Function
Your kidneys filter waste from your body and regulate salts in your blood. They also produce hormones and vitamins that direct cell activities in many organs and help to control blood pressure. When the kidneys aren't working properly, waste products and fluid can build up to dangerous levels creating a life-threatening situation.
Test instructions

This blood test should be completed on Day 3 of the menstrual cycle (which is the third day of menstrual bleeding).

Fast from all food and drink other than water for at least 8 hours, and no more than 12 hours prior to your test. Please note some collect centers require this test to be performed before 10am.

Print out the pathology form that we email you.

Take your form to one of our affiliated collection centres to have your sample taken - no need for an appointment. Please note that in some locations, collections for some specialist biomarkers may require a visit to a specific collection centre within a defined period. We recommend ringing in advance to confirm whether this may apply.
Ready. Set. Go!
for $1000 NZD